

Issue 02 · Volume 72 · February 2022
Original Article
Mahlooji MA et al.
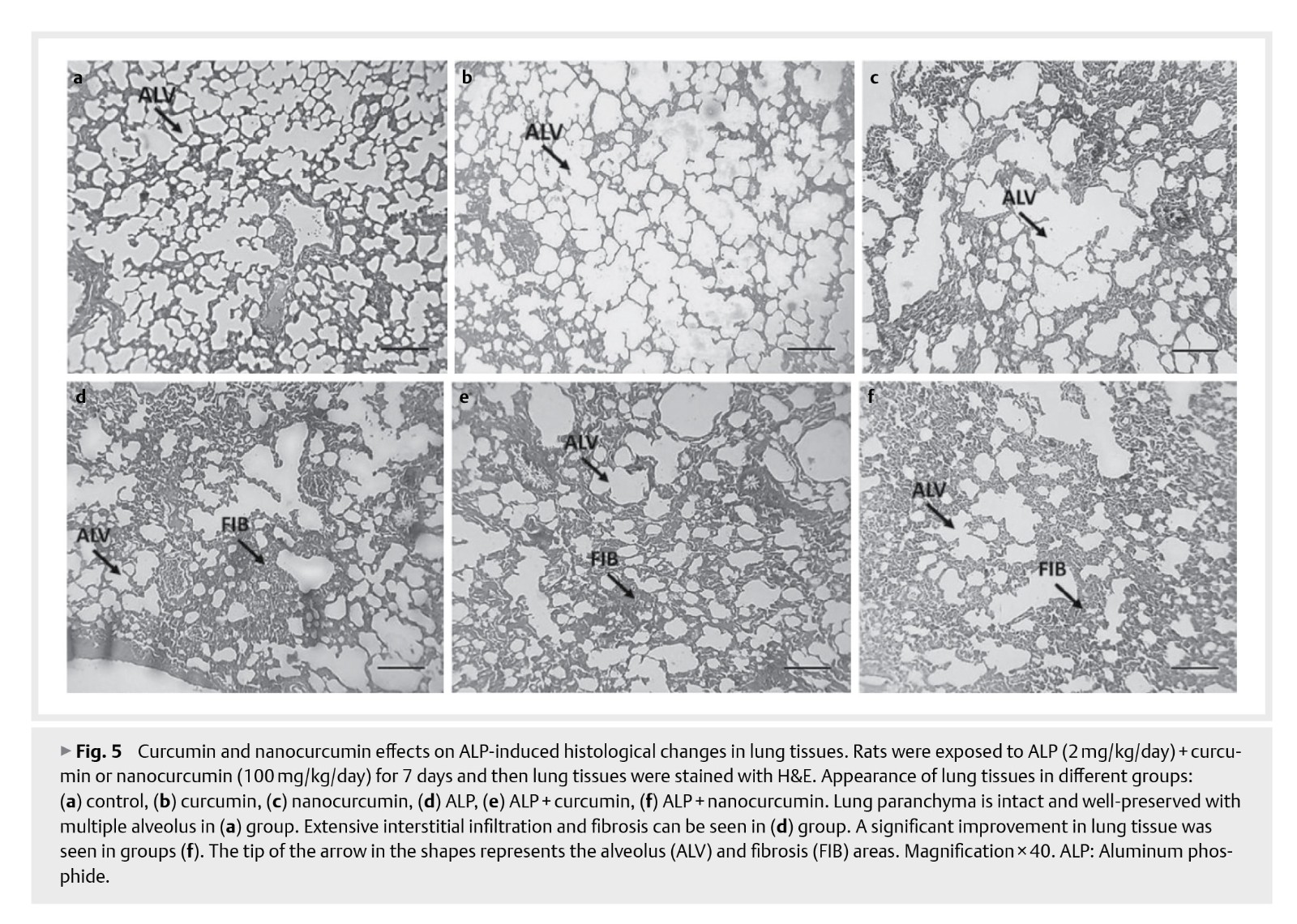
Aluminum phosphide (AlP) is widely used to protect stored food products and grains from pests and rodents. The availability of AlP, especially in Asian countries it has become a desirable factor to commit suicide. The phosphine produced from ALP is a very reactive radical and a respiratory inhibitor that causes oxidative damage. There is no dedicated antidote or effective drug to manage AlP-induced lung toxicity. The present study aims to evaluate and compare the protective effects of curcumin and nanocurcumin on ALP‑induced subacute lung injury and determine the underlying mechanism.
Review
Naz S et al.
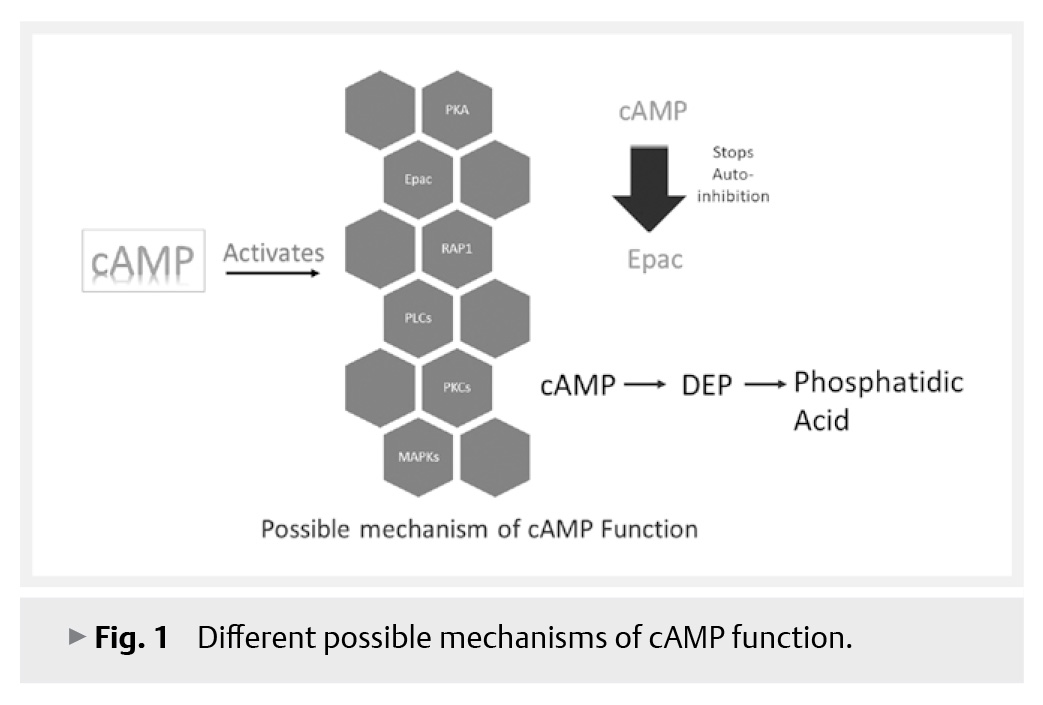
It is well recognized that cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling within neurons plays a key role in the foundation of long-term memories. Memory storage is the process that demands the movement of signals, neural plasticity, and the molecules which can transfer the signals from the sensory neuron to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons and later into the temporal region of the brain. The discovery of cAMP in 1958 as the second messenger also had a role in memory formation and other neural aspects. Further, in 1998 the scientists found that cAMP does not just activate protein kinase A (PKA) but also exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac) which has an active role to play in hyperalgesia, memory, and signaling. The cAMP has three targets, hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide modulated (HCN) channels, protein kinase A (PKA), and exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac). Different research has exposed that both PKA and HCN channels are significant for long-term memory creation. Epac is a cAMP-dependent guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the small G proteins including Rap1. However, slight information is there about the role of Epac in this process. The effects of cAMP are predominantly imparted by activating protein kinase A (PKA) and the more newly discovered exchange proteins are directly activated by cAMP 1 and 2 (EPAC1 and EPAC2). This review provides an insight regarding the function and role of both of these secondary messengers in memory and nerve signaling.
