
Directed Evolution Toward Nonstandard Amino Acids by a Decarboxylative Aldol Reaction
Contributor(s): Benjamin List, Marian Guillén
Ellis JM, Campbell ME, Kumar P, Geunes EP, Bingman CA, Buller AR. * University of Wisconsin–Madison, USA
Biocatalytic Synthesis of Non-Standard Amino Acids by a Decarboxylative Aldol Reaction
Nat. Catal. 2022; 5: 136-143
DOI: 10.1038/s41929-022-00743-0
Key words
whole-cell biocatalysis - decarboxylation - aldol reaction - amino acids - directed evolution
Significance
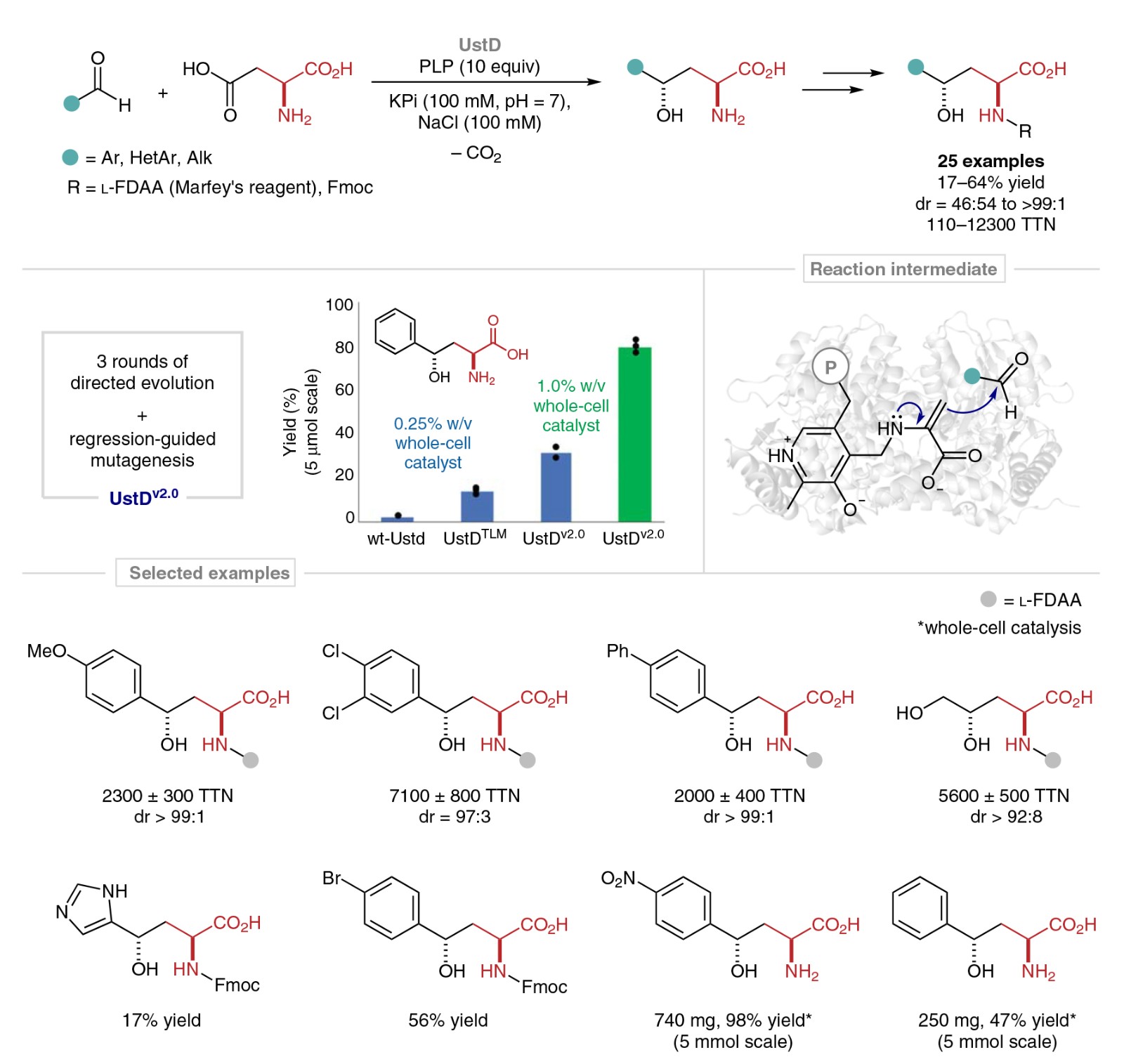
Buller and co-workers disclose an enantioselective synthesis of γ-hydroxy amino acids catalyzed by engineered variants of a pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzyme. Various products of C–C bond-forming reactions were obtained in moderate to excellent yields and enantioselectivities. The optimized enzyme UstDv2.0 is efficient in a whole-cell biocatalysis format, thereby eliminating the need for enzyme purification in gram-scale syntheses.
Comment
Unlike other classic aldolases, UstD is capable of decarboxylating the side chain of pyridoxal-bound l-aspartate to form a putative nucleophilic enamine intermediate, which renders the enantioselective C–C bond-forming reaction effectively irreversible. An X-ray crystal-structure analysis of UstDv2.0 revealed the active site and provides a foundation for probing the UstD mechanism. A broader scope of gram-scale whole-cell applications is anticipated.
