

Issue 03 · Volume 54 · March 2022
Endocrine Care
Gonen MS et al.
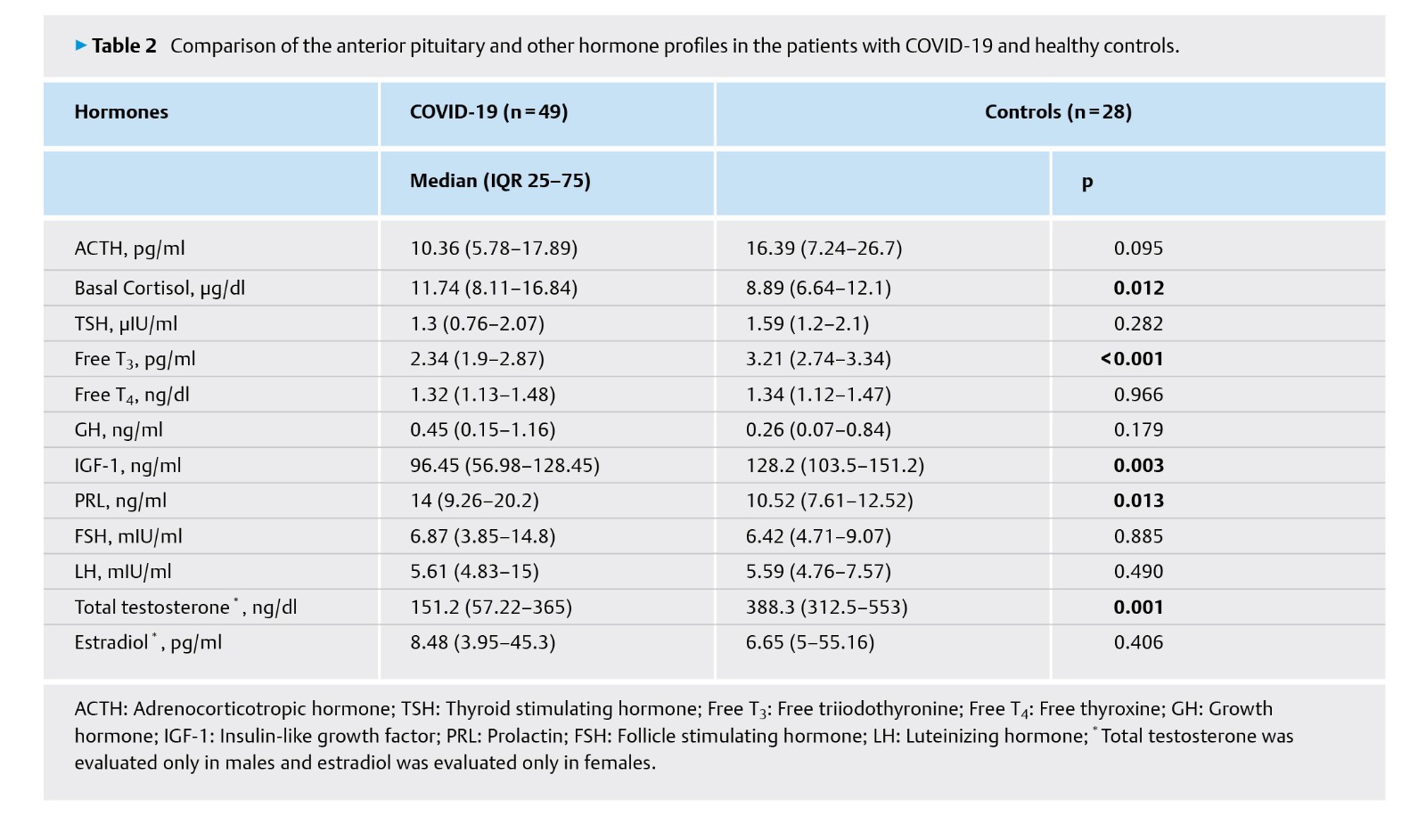
SARS-CoV-2 may affect the hypothalamic-pituitary axis and pituitary dysfunction may occur. Therefore, we investigated neuroendocrine changes, in particular, secondary adrenal insufficiency, using a dynamic test and the role of autoimmunity in pituitary dysfunction in patients with COVID-19. The single-center, prospective, case-control study included patients with polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-confirmed COVID-19 and healthy controls. Basal hormone levels were measured, and the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test was performed. Antipituitary (APA) and antihypothalamic antibodies (AHA) were also determined. We examined a total of 49 patients with COVID-19 and 28 healthy controls. The frequency of adrenal insufficiency in patients with COVID-19 was found as 8.2%. Patients with COVID-19 had lower free T3, IGF-1, and total testosterone levels, and higher cortisol and prolactin levels when compared with controls. We also demonstrated the presence of APA in three and AHA in one of four patients with adrenal insufficiency. In conclusion, COVID-19 may result in adrenal insufficiency, thus routine screening of adrenal functions in these patients is needed. Endocrine disturbances in COVID-19 are similar to those seen in acute stressful conditions or infections. Pituitary or hypothalamic autoimmunity may play a role in neuroendocrine abnormalities in COVID-19.
Review
The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Bone Health: State of the Art and New Recognized Links
Mendonça F et al.
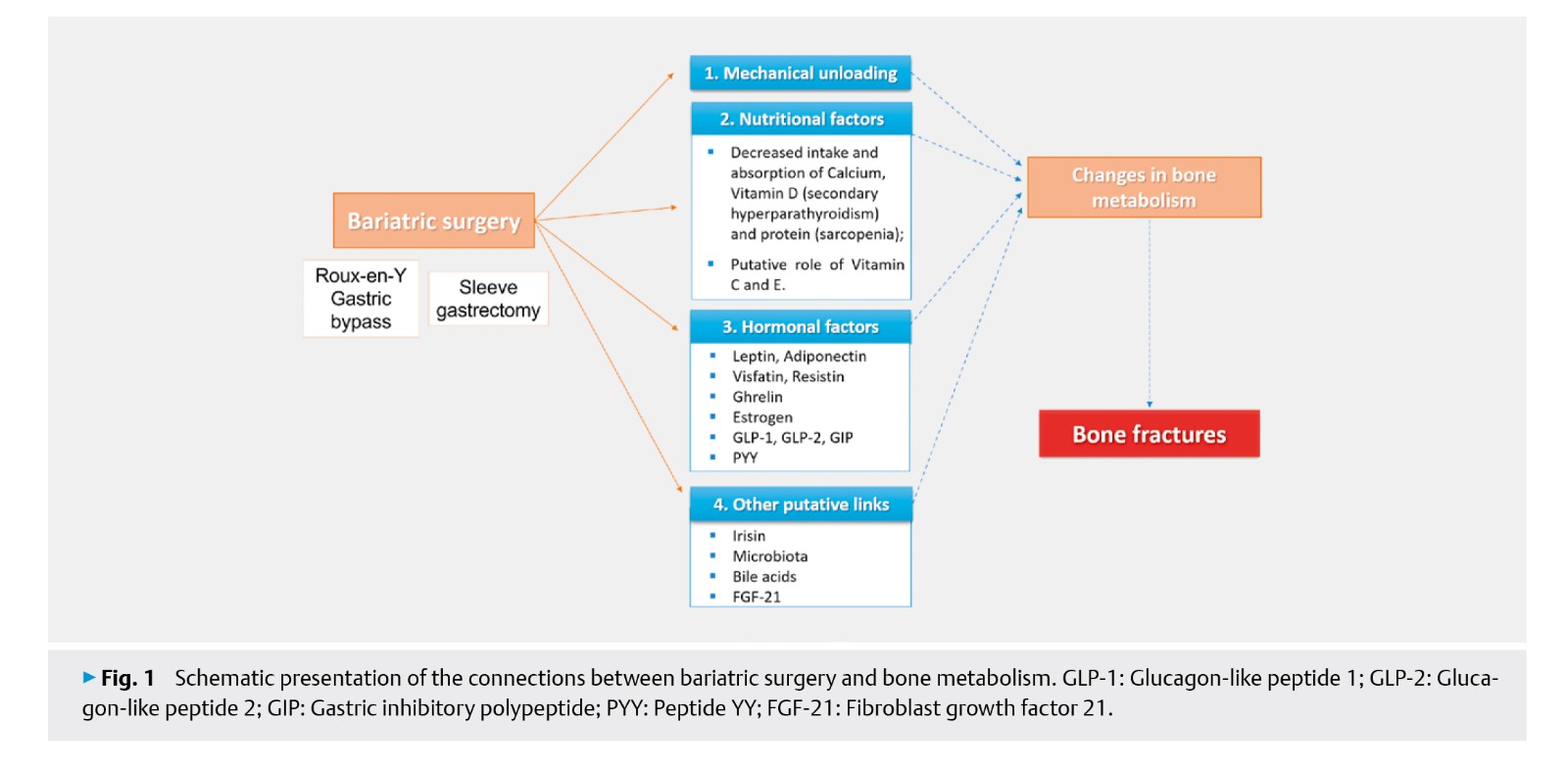
Bariatric surgery (BS) is the most effective therapy for severe obesity, which improves several comorbidities (such as diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, among others) and results in marked weight loss. Despite these consensual beneficial effects, sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (the two main bariatric techniques) have also been associated with changes in bone metabolism and progressive bone loss. The objective of this literature review is to examine the impact of bariatric surgery on bone and its main metabolic links, and to analyze the latest findings regarding the risk of fracture among patients submitted to bariatric surgery.
Endocrine Care
Wei Liu, Jingjing Zhang, Yaling Yang, Yinxin Jin, Zaizhao Li, Liting You, Jianguang Luo, Xin Su
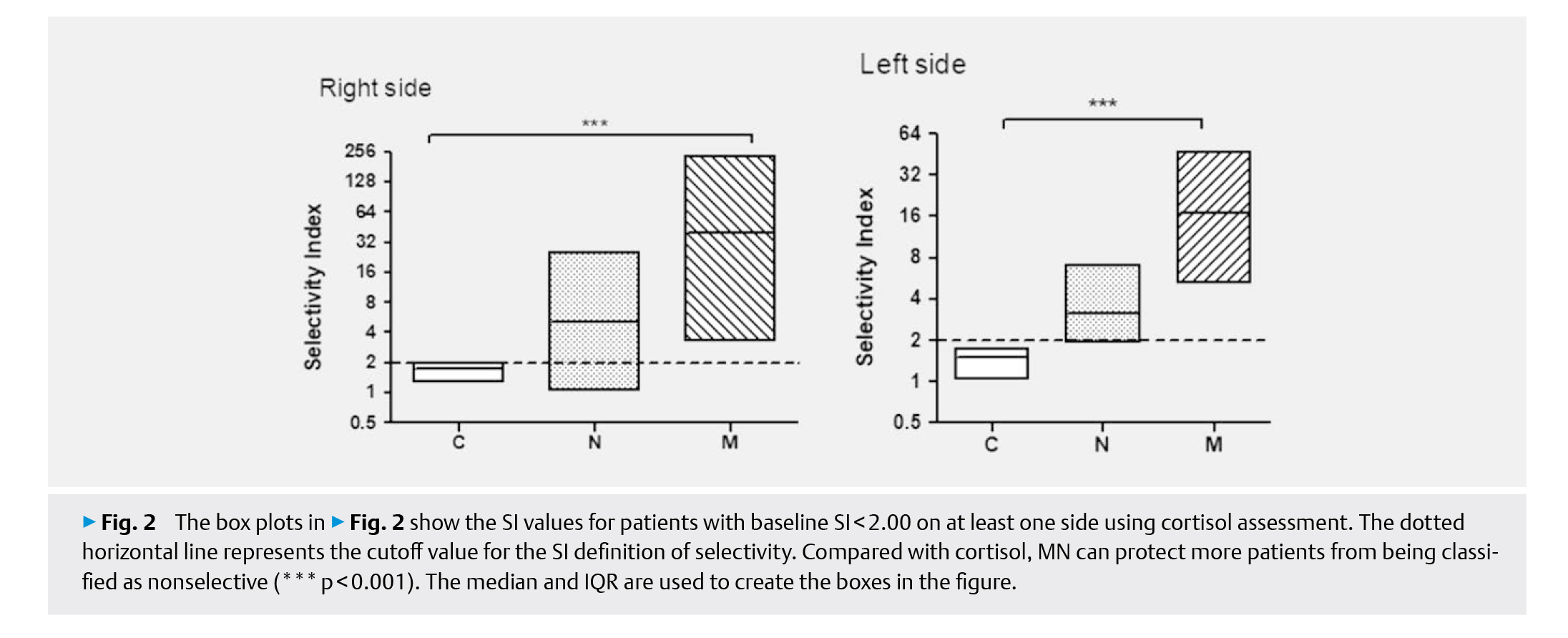
The aim of the study was to investigate the usefulness of metanephrine (MN) and normetanephrine (NMN) in bilateral simultaneous adrenal vein sampling (AVS) with and without ACTH stimulation. The study was conducted in a single referral center. Prospective recruited patients with PA were treated with AVS. The effects of cortisol, MN and NMN on selectivity catheterization were assessed and determined by lateralization. We enrolled 54 patients with PA who were treated with simultaneous bilateral AVS with ACTH. The Selectivity Index (SI) calculated by MN was higher than that calculated by other indicators (p<0.001), the catheterization success rate of MN at baseline was the same as that of cortisol after ACTH stimulation, and in lateralization diagnosis, MN was not inferior to cortisol. In conclusion, among the studied indicators, MN is the best index for determining the catheterization selectivity in AVS, especially in the absence of ACTH stimulation.
